Welcome to our industrial water learning center!
If you are looking for water usage statistics or facts and information on industrial water treatment methods, you have come to the right place. This industrial water learning center is packed full of useful industrial water treatment information. Keep reading to learn more about the uses and benefits of different types of water treatment equipment. We discuss commercial water softeners, dealkalizers, industrial reverse osmosis systems, and more.
Did You Know? Industrial Water Facts
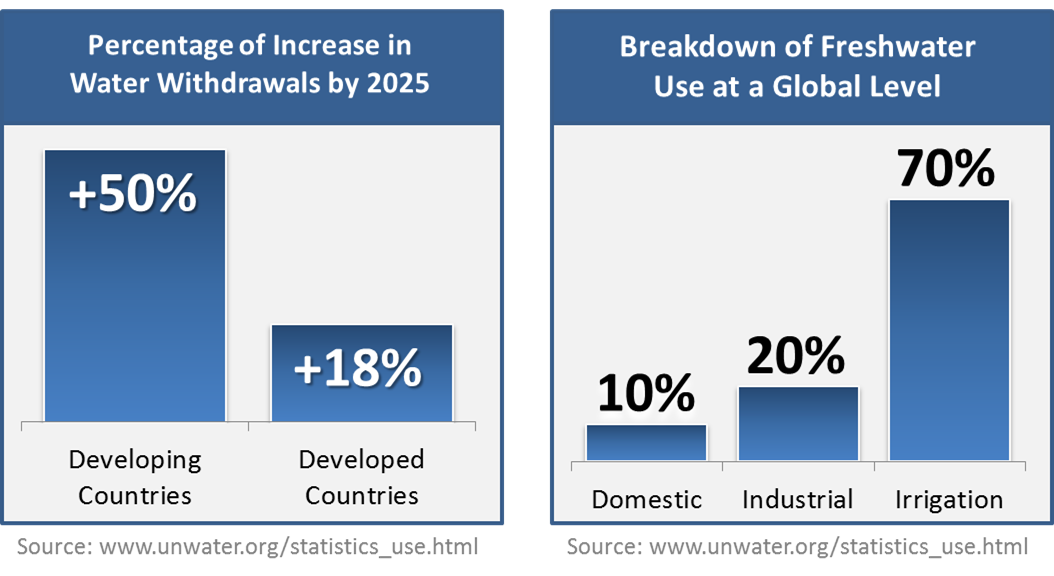
- Industry accounts for 20% of all freshwater use. (Source: World Water Assessment Programme)
- High-income countries, such as the United States, use 6 times more water for industrial purposes than low-income countries. (Source: United Nations World Water Development Report, 2003)
- Louisiana tops the list of states that use the greatest amount of freshwater for industrial purposes. (Source: The Centers for Disease Control)
- Globally, there are 215 international rivers and 300 groundwater basins shared by two or more countries. (Source: Water Industry News)
Frequently Asked Water Treatment Questions
Visit our Industrial Water Treatment FAQ webpage for answers to frequently asked questions about boiler feedwater pre-treatment, RO filtration and more.
Water Softeners
Industrial and commercial-grade water softeners are typically used by apartment complexes, hospitals, factories, and manufacturing plants. They use water softeners to prevent scale build-up from clogging pipes and machinery. Scale is a by-product of hard water, which if left untreated reduces the efficiency of hot water boilers, cooling towers, and steam-powered equipment. Industrial water softeners work to reduce hard water build-up by removing scale and depositing minerals from the water. Water softening is an economical approach to treating hard water that can help reduce operating expenses and extend the lifeline of equipment.
Dealkalizers
Dealkalization is the process of extracting alkaline ions from water.
Why is Alkalinity Important?
Alkalinity is a measurement of water’s ability to neutralize acids. There are three types of alkaline compounds that may be present in water: carbonate, hydroxide, and bicarbonate (which can be found in baking soda).
The three primary methods for removing alkaline ions and reducing alkalinity in water are:
- Lime Softening: This method of softening utilizes controlled amounts of calcium hydroxide to accelerate the hardening of calcium carbonate precipitate. During this process, the pH level of the water is raised to about 10. This allows the precipitated alkalinity to be filtered from the water as sludge. Lime softening is relatively inexpensive and reliable, but the process is tedious and requires chemical usage and disposal.
- Nanofiltration: This filtration process uses a semipermeable membrane to filter out divalent alkaline ions from water. Nanofiltration produces high-quality, alkaline-free water but is relatively expensive and requires the water to first be pretreated to remove other contaminants that may be present.
- Dealkalization: Dealkalization is an ion exchange process that works similarly to water softening. In dealkalization, an ion exchange resin bed exchanges chloride ions for sulfate, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions in water. There are several different dealkalization methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits of Dealkalization:
Dealkalizers are frequently used by industrial businesses to reduce the level of alkalinity in boiler water feed. When water alkalinity is too high, the boiler water will begin to foam and carryover, resulting in increased occurrences of boiler blowoff and boiler blowdown. By using dealkalizers for boiler water pretreatment, industrial businesses are able to reduce operating costs and boiler blowdown. In addition, the removal of carbonate and bicarbonate alkalinities by dealkalizers reduces the number of corrosive elements carried over in the steam that passes through process equipment and return lines. Dealkalization is also commonly used to treat water pumped through cooling towers as a means of lowering chemical usage and preventing corrosion.
Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis systems are one of the most effective means of recycling industrial wastewater. RO is often used by restaurants, car wash facilities, healthcare clinics, and industrial printing facilities to strip metals, minerals, viruses, and microorganisms from water. Plating facilities and semi-conductor manufacturing plants can reduce water use and minimize operating costs, by utilizing reverse osmosis to treat and recycle rinse water. When combined with other water pretreatment and filtration methods, RO systems may be used to produce dialysis water for hemodialysis patients and purified water for laboratory use.
Filtration Systems
The purpose of water filtration systems is to remove sediments and solid particulates from water. In the industrial field, water filtration systems are typically used in conjunction with a water softener or dealkalizer. Water is often pretreated with chemicals and conditioned prior to passing through a filtration system.
There are three main methods of industrial water filtration: rapid gravity, pressure, and upflow. Rapid gravity filtration is typically used by municipal water treatment plants in the treatment of drinking water. Pressure water filtration systems are used for industrial applications where water must be rapidly forced through the filtration medium (i.e. to prevent heat loss to boiler water feed). Upflow filtration systems are a type of pressure filter where water is initially pumped to the bottom of the filtration system and rises up through the filtration medium.
Applications for Industrial water treatment: boiler & cooling tower feed, pretreatment, laundry, food service, sterilization, domestic hot, drinking water, ice & vending machines, atrium plants, swimming pool, spa, classroom & research labs, machining, grinding, washing, smelting, stamping, processing, cooling, petroleum, power generation, agricultural processing, chemical production, petroleum refinement, municipal wastewater, and municipal drinking water. Customers can rely on one of the most well-known brands across all markets.